Mobile Robot Reinforcement Learning with Isaac Lab
Overview
Isaac Lab is a framework developed by NVIDIA for robot learning that integrates with Isaac Sim for photo-realistic simulations. The core idea is to develop "environments" using the Isaac Lab API. These environments define a task for a robot to learn, such as a quadruped learning how to walk forward. Then, when writing a script that defines a neural network architecture and a training function, this environment is passed in as a parameter when this training script is ran.
For this project, 3 Isaac Lab environments were developed for training a quadcopter and a rover on navigating to some goal, when given some input (x, y, z) waypoint.
Environment Creation Methodology
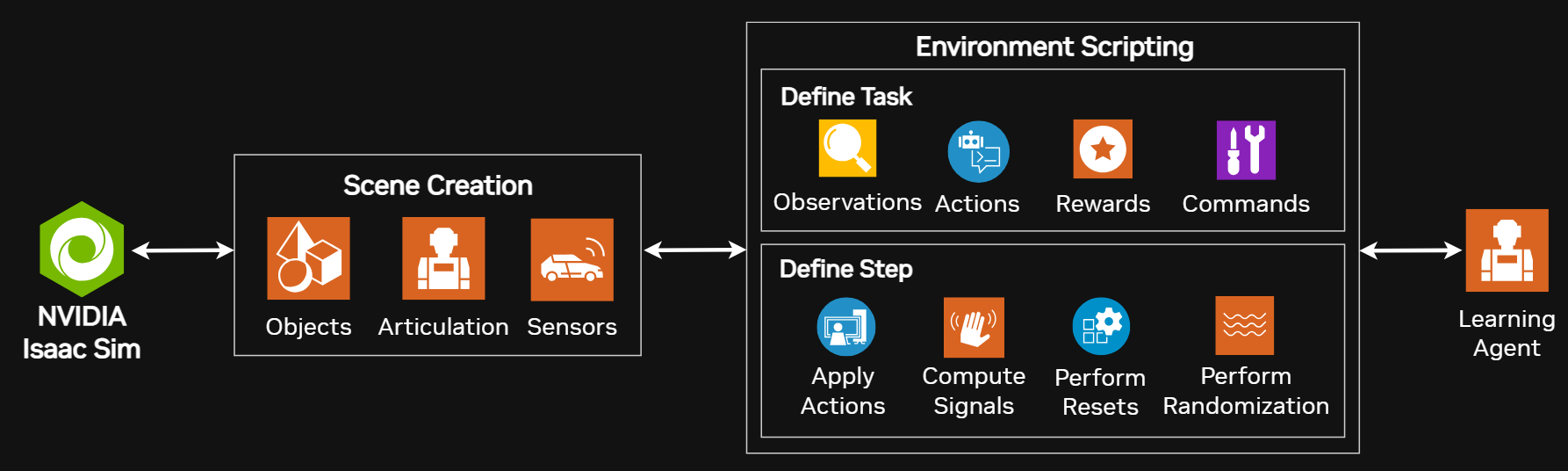
To engineer an Isaac Lab environment, these are the most vital functionalities that were implemented:
- Hyperparameter Tuning: There are a number of hyperparameters that were tuned for best performance. An extremely critical hyperparameter is the number of robots/environments being trained in parallel. The more robots there are being trained in parallel, the more data there will be that can be collected during rollout, which allows for much faster training. However, this is constrained by factors such as available memory.
- Reward: Using the API, information about each robot's state can be accessed. During parallel training, rewards (or penalties) are computed per robot from those states—for example, rewarding forward motion in proportion to forward velocity.
- Episode Termination and Reset Functions: If the robot enters an unrecoverable state (e.g., flips onto its back and can’t move), the episode terminates to avoid wasting compute. The environment then resets—in this case, returning the robots to their starting poses and sampling new navigation goals.
- Sensor Configuration and Observation Function: Sensors readings are the inputs to the robot's control policy and so they have to be configured before training. GPS is simple since the simulator has perfect state information about where the robot is and where the goal is. For a camera, an Isaac Lab camera object must be instantiated. This requires setting the camera type (depth, rgb, etc), the pixel height and width of the image, and where the camera is physically located on the robot asset in the simulation. The observation function takes in raw sensor readings as input and decides how to pre-process them before they are passed into the control policy.
- Control Policy Architecture: The control policy is a neural network trained with Proximal Policy Optimization, and its architecture (as well as that of the value function) was written out with PyTorch. Both the policy and value function have a shared backbone, but differ in their final fully connected layers. A yaml file can also be used, which was the case for the quadcopter's control policy as the quadcopter didn't need convolutional layers.
- Simulation Scene Setup: Setting up the simulation scene requires placing the required assets into the simulator. For example, the terrain (hilly terrain or a flat floor) is defined, the robots have to be placed into a valid starting position in the scene, and props (in this case, goal waypoints) have to also be placed in their appropriate position. For variable-height terrain, code must be written that quaries the height of the terrain at some (x,y) coordinate, so that the robot can be safely placed on the terrain without accidentally clipping into it.
Environment Demonstrations
Iris Quadcopter Fly-To-And-Hover
Explanation: The quadcopter observes its body frame linear velocity, body frame angular velocity, and the distance between itself and the goal for decision-making. The control policy is a simple feed-forward MLP.
Jackal Rover Grid-World Navigation
Explanation: The rover's initial pose has it starting off not being able to see the goal marker, so it explores the space until its camera is able to detect the goal. The control policy is a simple feed-forward CNN and MLP combination that uses 3-channel RGB images and GPS readings for decision-making.
Jackal Rover Variable-Height Terrain Navigation
Explanation: Just like with the grid-world, the rover explores its space until it is able to see the goal waypoint. The neural network architecture and sensor configurations remain unchanged. This control policy is able to navigate to (x,y,z) goals, rather than just (x,y) goals.